Innovation: NDT prediction of surface hardness and case depth based on AI
05/24/2024
At Control 2024 ibg NDT Technologies launches it latest Innovation. Based on the rich data steaming from its well-known eddy current instrumentation it has developed non-destructive solutions to predict surface hardness and the case depth / gradient at the speed of inline systems combining eddy current and AI.
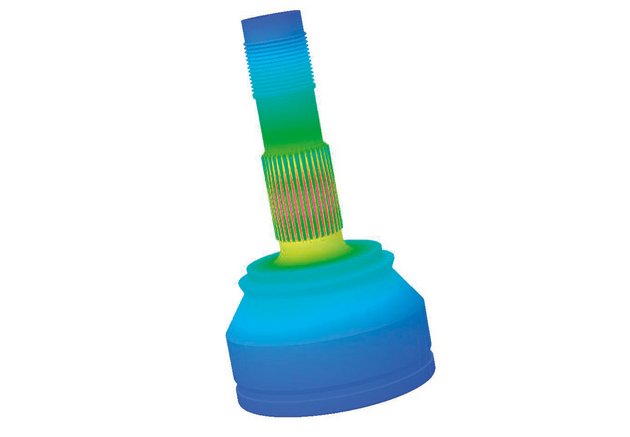
Situation
Heat treatment and similar procedures have the intention to create a defined structure of the metal, which in in return should lead to desired mechanical characteristics. Hardness is traditionally one accepted measurement of this structure. In some cases, only parts or layers are laid out for heat treatment, so inductive heat treatment is used. The results can be measured up until today only by destructive testing in laboratories, requiring skill, time, and specific equipment.
Problem
Due to the high costs and efforts, usually only a small number of samples out of high-volume batches are measured. That is a severe limitation in many aspects and a waist of resources.
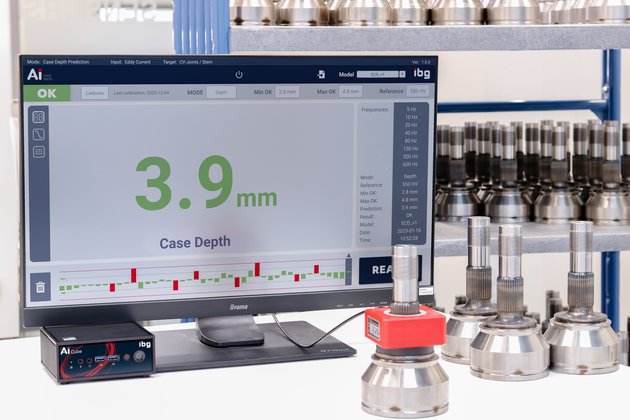

Innovation
Now the limitations of destructive testing have been overcome within the lab and the new method can even be moved into the line. Eddy current results from the ibg instrumentation in combination with AI models and the database of ibg are used to predict surface hardness and hardening depth of specific component geometries such as CV joints for EV cars. The new method operates at high speed, allowing intact in-line testing, and retrofit.
Implications
The cost / time efficiency and the reliability of the new AI enhanced method allows a dramatic increase of numerical data points on the results of heat treatment.
- It saves labor and cost by reducing destructive testing or moving remining destructive testing away from night shifts.
- It increases “peace of mind” by more testing up to 100% inline.
- It increases the value of products by allowing for “100% tested” parts.
- It provides data to optimize the process of heat-treatment in terms of quality, tolerances, energy, and CO2 emission.

